Analyzing BLE
1. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) internals
Introduction and Terminology
The way BLE devices discover and connect to each other is determined through the Generic Access Profile, or GAP for short.
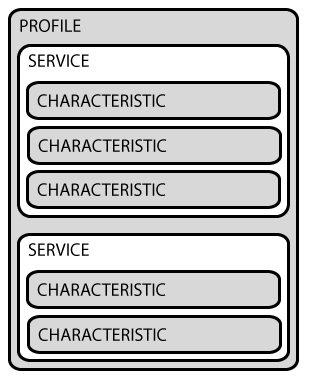
The Generic Attribute Profile, or GATT, determines how two devices transfer data back and forth, once the devices have discovered and connected to each other using GAP. GATT uses the Attribute Protocol, or ATT, to store Services and Characteristics in a simple lookup table. Services divide data into logical chunks, and each Service has a UUID. Services consist of Characteristics, which are the data points themselves. Like Services, each Characteristic has a UUID.
Note that BLE peripherals can only be connected to one central device at any given time. The central device however, can be connected to several peripheral devices at once.
Example
A profile has Service A (for example heart rate in UUID format) and Service B (for example blood pressure in UUID format).
Service A and Service B consist of characteristics, which in turn consist of values and descriptors.
Other profiles are structured similarly.
 [2]
[2]
Service
Structure:
attr handle | (first handle id for the service)
end grp handle | (last handle id for the service)
uuid | (first 8-digit from left hand side specifies service name)
All the currently registered UUIDs by Bluetooth and their corresponding service names can be found in the Bluetooth SIG documentation. Custom services are not defined there, however.
- Characteristics
- Structure
- handle
- char properties
- char value handle
- uuid
- Value: Descriptor is a hex encoded ASCII data
- Structure
- BLE authentication (association process)
- Broadcaster device
- broadcast to announce availability
- collect and monitor data
- Observer device
- observe broadcasts
- if it is an interested broadcast, send a connection request to the peripheral
- Peripheral device
- if peripheral accepts the request, observer and peripheral are connected
- based on the pairing mechanism
- data transmission starts each other
- Broadcaster device
- Pairing mechanisms (Pairing encryption)
- JustWorks (JW)
- without display or small display without keyboard
- key is 000000
- Numeric comparison
- shows the same number on both devices
- asks for yes or no
- Passkey
- 6-digit passcode
- (easy to brute force)
- Out of band
- shares the pin using an out of band channel like NFC
- JustWorks (JW)
2. BLE pentest objectives
- Sniffing
- Reading
- Modifying characteristics (change behavior of the device by remotely controlling)
3. Interacting with BLE devices
- Plug in BLE adapter dongle on analysis computer
-
Get Blootooth Address (BD_ADDR)
hciconfig -
Search for BLE devices around (via hcitool or Blue Hydra)
hcitool lescan -
Connect to target beacon (via Gatttool utility)
gatttool -I -b <beacon address> -
List the BLE services
primary -
List the service characteristics
characteristics -
Read characteristics value and descriptor
char-read-hnd <char value handle> - Decode hex to ASCII
4. Modify data
- In order to modify something, functionality of the device is well-understand
- Then how these functionality is stored on device as values are identified
- Example I
- BLE devices disconnects from mobile application in every X seconds
- Then re-connects again, this mechanism is known as heart-beat
- If heartbeat does not happen, a notification appears or sound triggered
- Attacker may want to modify the connection time to unlimited
- Therefore mobile app will not identify BLE device is stolen or broken
- Example II
- mobile app tracks the distance of an object
- if it goes across the range, mobile app makes a buzzer
- attacker may want to prevent buzzer not to notice owner
-
List all handles
chr-desc <attr handle> <end group handle> - Check for Bluetooth SIG documentation (to understand functionality)
- identify services defined by manufacturers and by SIG
-
Read characteristics value and descriptor
char-read-hnd <char value handle> -
Update characteristics value and descriptor
char-write-hnd <char value handle> <a char value same as to original format>
5. Sniffing BLE traffic
- In order to understand the functionality of services defined by manufacturers
- sniff the BLE traffic
- press any buttons of the device to capture functionality
- Ubertooth One
- download and install ubertooth utility
-
sniff traffic
ubertooth-btle -f -t <target device BD_ADDR> -
sniff traffic and dump into a pcap file
ubertooth-btle -f -t <target device BD_ADDR> - c ble-dump.pcap -
Relevant data
Access address (AA) used to manage link layer Channel Index dedicated advertising channel Packet PDU Type ADV_IND ADV_DIRECT_IND ADV_NONCONN_IND ADV_SCAN_IND SCAN_REQ SCAN_RSP CONNECT_REQ AdvA 6-byte advertising address (usually BD_ADDR of the device) ScanA 6-byte scanner address -
Advertising PDUs
ADV_IND Connectable Undirected Advertising ADV_DIRECT_IND Connectable Directed Advertising ADV_NONCONN_IND Non-Connectable Undirected Advertising ADV_SCAN_IND Scannable Undirected Advertising -
Scanning PDUs
SCAN_REQ Scan request from the mobile app SCAN_RSP Scan response from the target device -
Initiating PDUs
CONNECT_REQ Connection request - Wireshark
- set DLT_USER (in Preferences > Protocols) to btle
-
filter only ATT packets
btl2cap.cid==0x004 - set DLT_USER (in Preferences > Protocols) to btle
- filter Write requests
- find the data is written to which Handle
- examine the interested packet containing write request
- BLE Link Layer
- Bluetooth Attribute Protocol
- Understand Value field
- compare Value field of different packets to identify which bits change
- the changed field are the user actions
- determine your Value
- Replay packet
- BTLEJuice utility (web GUI)
- sniffs/modifies/replays BLE packets
- BTLEJuice utility (web GUI)
- Write the value to the device
- gatttool “char-write-req”
Sources
[1] A Developer’s Guide To Bluetooth. Bluetooth Blog. Martin Woolley. 2016-11-10. https://www.bluetooth.com/blog/a-developers-guide-to-bluetooth/. (Fetched 2021-06-24)
[2] Introduction to Bluetooth Low Energy. adafruit learn. Kevin Townsend. 2014-03-20. https://learn.adafruit.com/introduction-to-bluetooth-low-energy. (Fetched 2021-06-24)